Concrete is a construction material composed of cement, aggregate (generally a coarse aggregate made from gravel or crushed rocks such as limestone, or granite, plus a fine aggregate such as sand), water, and chemical admixtures. In this article definition of the density of concrete is provided and the value of concrete density is provided from various sources.
Concrete Definition:
Concrete, an artificial stone-like mass, is the composite material that is created by mixing binding material (cement or lime) along with the aggregate (sand, gravel, stone, brick chips, etc.), water, admixtures, etc in specific proportions. The strength and quality are dependent on the mixing proportions
Density is an important parameter for concrete. The density of concrete varies depending on the proportions of the ingredients used to make it. A typical concrete mix contains cement, water, sand, and gravel. The proportion of each ingredient varies depending on the purpose of the concrete. For example, a concrete mix used for making sidewalks would have a different proportion of ingredients than a mix used for making a foundation for a building.
High Density Concrete
High density concrete is a type of concrete that has a higher density than regular concrete. The increased density is usually achieved by adding weight to the concrete mix. The added weight can come from any number of materials, but the most common is to add a heavy aggregate such as gravel or sand. Other materials that can be used to increase the density of concrete include iron or steel fibers, and even plastic or glass fibers.
Bulk Density of Concrete
The bulk density or unit weight of concrete is the mass or weight of the concrete that is required to fill a container of a specified unit volume.
\[Bulk\; Density=\frac{Mass}{Volume}\;in \; kg/m^{3}\; or \;lb/ft^{3}\]
Key Features:
- If the volume is unit then, Bulk Density= Mass.
- Unit in kg/m3 or lb/ft3. lb/ft3 is also used as pcf. To convert between different density units, visit >> All Density Conversions.
- In this definition, the volume contains both the concrete and the voids between concrete particles.
- Here, the Standard test method for determining the bulk density of concrete is given in ASTM C138 / C138M (AASHTO T 121M/T 121). [1]
Standard Values of Concrete Density
We have found the following sources where the standard value of the density of concrete is provided.
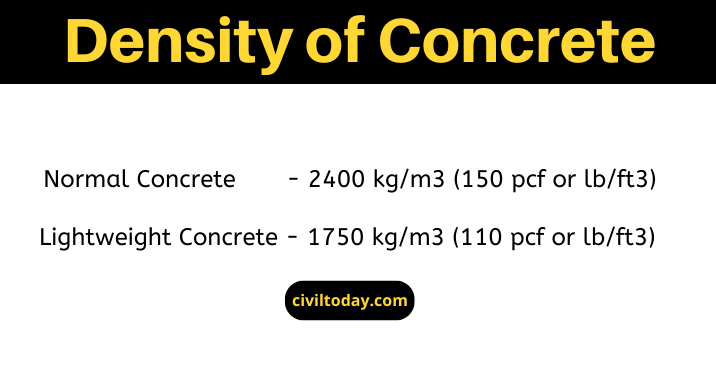
The density of normal concrete is 2400 kg/m3 (150 pcf or lb/ft3) and the density of lightweight concrete is 1750 kg/m3(110 pcf or lb/ft3)
Typical density of concrete 2.3 g/cm3 (143.6 pcf or lb/ft3 / 2300 kg/m3)
Volume generally assumed for the density of hardened concrete is 150 lb/ft3 (2400 kg/m3)
Density in Place: Density of normal CLSM in place typically ranges from 90 to 125 pounds per cubic foot (1840 to 2320 kg/cubic m)
Density Concrete 2242 kg/m^3
While conventional concrete has a density of about 2300 kg/m3, lightweight concrete has a density between 160 and 1920 kg/m3.
The concrete must be of a lightweight nature, with a mass of not greater than 1.5 kg/100 mm cube or a density of 1500 kg/m3
Density (kg/m3) 1450–1850
Typically, concrete has a density of 150 pounds per cubic foot, which means that a block of concrete that is one foot wide, one foot long, and one foot high would weigh 150 pounds. Water has the density of only 62.4 pounds per cubic foot.
References
- ASTM C138 / C138M - 17a Standard Test Method for Density (Unit Weight), Yield, and Air Content (Gravimetric) of Concrete Standard Test Method for Density (Concrete Unit Weight), Yield, and Air Content (Gravimetric) of Concrete & AASHTO T 121M/T 121 Standard Method of Test for Density (Unit Weight), Yield, and Air Content (Gravimetric) of ConcreteStandard Method of Test for Density (Unit Weight), Yield, and Air Content (Gravimetric) of Concrete

